审稿专家:左小霞
解放军总医院第八医学中心营养科主任
参考文献
[1] Davis C. From passive overeating to "food addiction": a spectrum of compulsion and severity[J]. ISRN Obesity, 2013, 2013: 535917.
[2] 帕特里克·霍尔福德. 营养圣经[M]. 范志红, 等译. 北京: 北京出版社, 2014.
[3] 李玉琳. 大脑奖赏系统在高脂饮食诱导肥胖C57BL/6小鼠不同饮食干预中的作用[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2009.
[4] 苏俭生, 韩雯斐, 延莉, 等. 年轻小鼠咀嚼刺激长期改变对焦虑和认知的影响[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2011, 38(7): 615-625.
[5] Onozuka M, Fujita M, Watanabe K, et al. Mapping brain region activity during chewing: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study[J]. Journal of Dental Research, 2002, 81(11): 743-746.
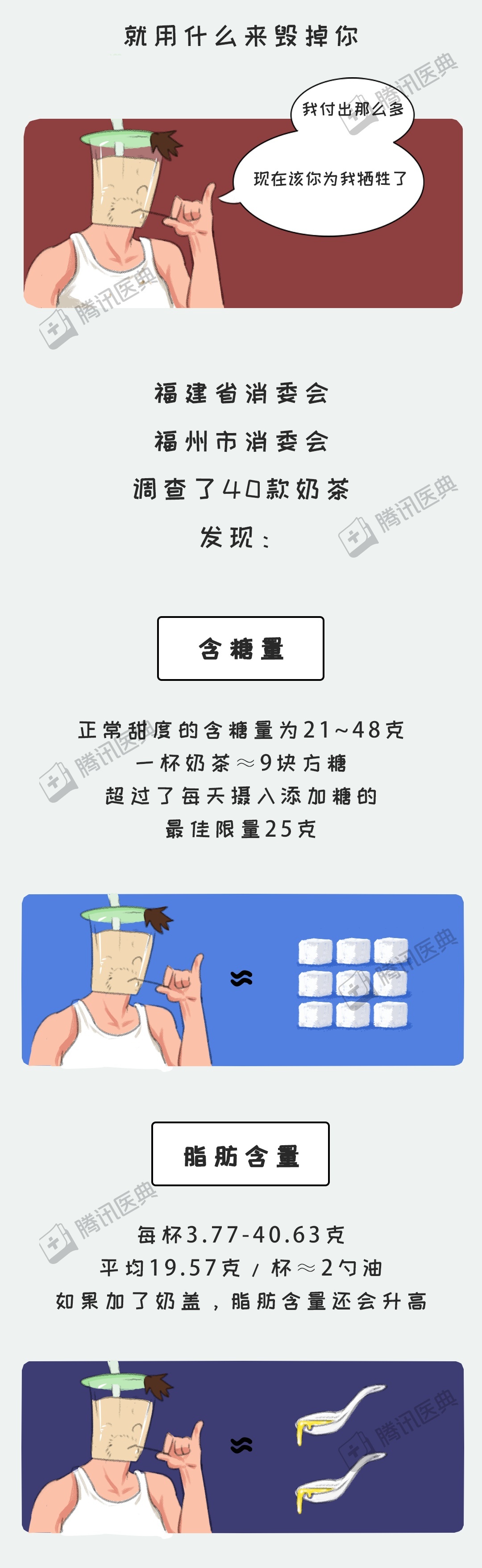
[6] 中国消费者报. 福州消协40款奶茶大检测: 奶茶没有奶, 无糖却含糖[EB/OL]. (2019-11-17)[2023-10-27]. https://www.guancha.cn/politics/2019_11_17_525436_s.shtml.
[7] 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食指南(2022)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2022.
[8] Watson E J, Coates A M, Kohler M, et al. The relationship between caffeine, sleep, and behavior in children[J]. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 2017, 13(4): 533-543.
[9] 上海市消费者权益保护委员会. 现制奶茶, 那些你不知道的事儿[J]. 食品与生活, 2017(8): 36-37.
[10] EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on the safety of caffeine[J]. EFSA Journal, 2015, 13(5): 4102.
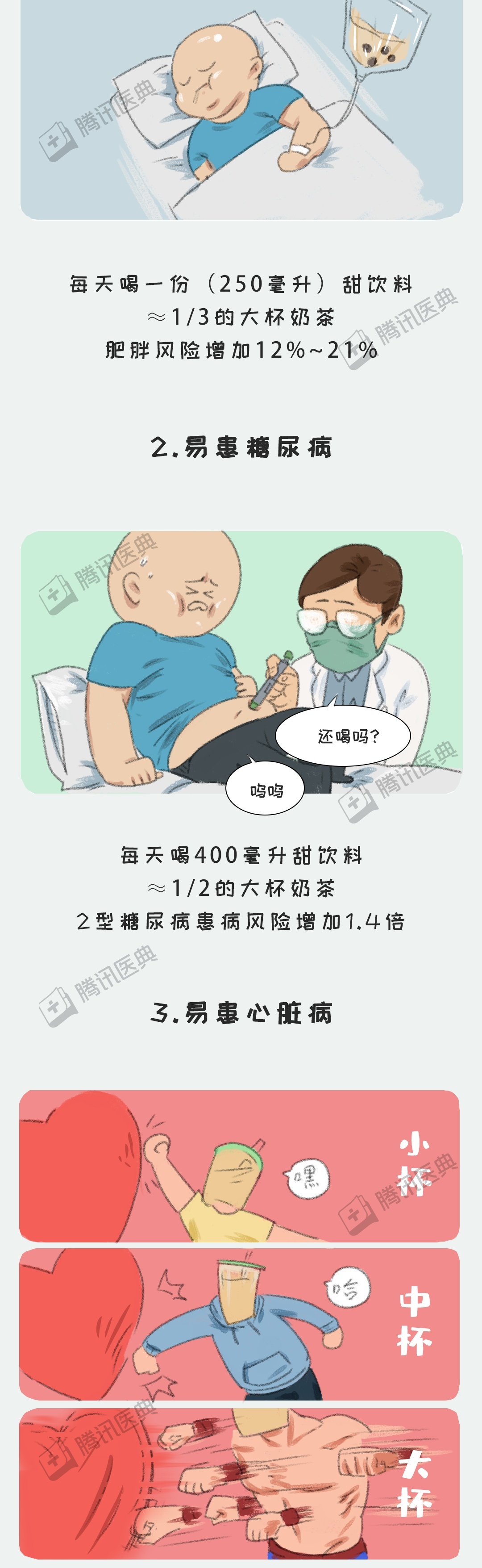
[11] Qin P, Li Q, Zhao Y, et al. Sugar and artificially sweetened beverages and risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. European Journal of Epidemiology, 2020, 35(7): 655-671.
[12] LofvenborgF J E, Andersson T, CarlssonN P O, et al. Sweetened beverage intake and risk of latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) and type 2 diabetes[J]. European Journal of Endocrinology, 2016, 175(6): 605-614.
[13] Collin L, Judd S, Safford M, et al. Abstract P235: Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption is associated with increased mortality risk in US adults[J]. Circulation, 2018, 137(Suppl_1): AP235.
[14] Kashino I, Kochi T, Imamura F, et al. Prospective association of soft drink consumption with depressive symptoms[J]. Nutrition, 2021, 81: 110860.
[15] 中国营养学会. 食物与健康: 科学证据共识(2016)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016.
*腾讯医典内容团队出品
订阅后可查看全文(剩余80%)